Introduction to FDM, OFDM, OFDMA, SOFDMA
OFDM has been in theory for decades but just entered real world
applications in recent years thanks to the availability of modern chips that can
handle complex digital signal processing. Wireline and
wireless, fixed and mobile communications or networking
technologies have chosen OFDM to achieve higher data rate (what is
called broadband). Examples of such technologies are: ADSL, HomePlug AV, WiMedia UWB, Wi-Fi
(802.11a/g), WiMAX.
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA)
Like OFDM,
OFDMA employs multiple closely spaced sub-carriers, but the sub-carriers are divided into groups of
sub-carriers. Each group is named a sub-channel.
The sub-carriers that form a sub-channel need not be adjacent. In the downlink,
a sub-channel may be intended for different receivers. In the uplink, a
transmitter may be assigned one or more sub-channels.
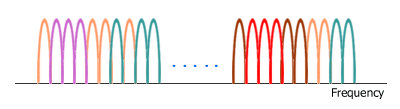
Picture. Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access
Sub-carriers with the same color represent a sub-channel.
Subchannelization defines sub-channels that can be allocated to subscriber
stations (SSs) depending on their channel conditions and data requirements.
Using subchannelization, within the same time slot a Mobile WiMAX Base
Station (BS) can allocate more transmit power to user devices (SSs) with lower SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio), and less power to user devices with higher SNR. Subchannelization also enables the BS to allocate higher power to
sub-channels assigned to indoor SSs resulting in better in-building
coverage.
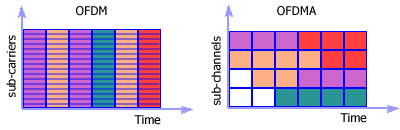
Picture. Uplink Subchannelization in WiMAX
In OFDM, only one SS transmits in one time slot.
In OFDMA, several SS's can transmit at the same time slot over several
sub-channels.
Subchannelization in the uplink can save a user device transmit power
because it can concentrate power only on certain sub-channel(s) allocated to
it. This power-saving feature is particularly useful for battery-powered
user devices, the likely case in Mobile WiMAX.
|