Internet Access Guide : WiMAX
For Fixed WiMAX, the 802.16-2004 is
harmonized with similar work by the European standard body, i.e. ETSI HiperMAN. The 802.16-2004 supports LOS
(line-of-sight) fixed
wireless access (FWA) in 10 - 66 GHz licensed frequency bands using
single carrier air interface. The two multi-carrier air interfaces
of Fixed WiMAX (i.e. OFDM and
OFDMA) support
LOS and NLOS applications in licensed and
license-exempt sub-11 GHz bands. The first Fixed WiMAX
profiles use OFDM with 256 carriers as its PHY (physical layer)
in the licensed 3.5 GHz band using a pair of 3.5 MHz or 7 MHz
TDD/FDD channels and
the unlicensed 5.8 GHz band using a 10 MHz TDD channel.
Meanwhile, Mobile WiMAX will operate in sub-6 GHz bands and
support scalable channel bandwidths from 1.25 MHz to 20 MHz over
SOFDMA (Scalable OFDMA) air interface. Release-1 Mobile WiMAX profiles
cover 5, 7, 8.75, 10 MHz channel bandwidths for licensed spectrum
in the 2.3 GHz, 2.5 GHz and 3.5 GHz bands.
Even though with PHY and MAC not fully compatible with Mobile
WiMAX specification, WiBro (Wireless Broadband) which is the
Korean implementation of IEEE 802.16e, is included as one of
Mobile WiMAX profiles. WiBro operates in the 2.3 GHz band over an
8.75 MHz TDD-channel. More details of Fixed and Mobile WiMAX system profiles can
be found on this page.
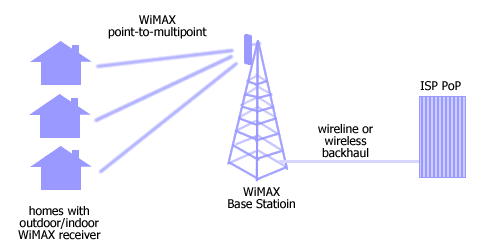
Picture: WiMAX Point-To-Multipoint (PMP) application
WiMAX MAC (media access control) sublayer supports
point-to-multipoint (PMP) and optionally mesh topology. In PMP
mode, traffic only occurs between Base Station (BS) and Subscriber
Stations (SSs) while in mesh mode, traffic can occur directly
between SSs. WiMAX
supports traffic scheduling, dynamic bandwidth allocation and QoS (Quality
of Service) per service
flow, which guarantees every type of traffic will be handled with
its associated bandwidth, latency, jitter, and priority
requirements. Therefore, WiMAX can deliver toll quality VoIP while
maintaining best effort traffic such as e-mail and web browsing at
the same time.
Every WiMAX traffic is encrypted using DES (Data Encryption
Standard) or AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
for securing its transmission over the air. The
encryption keys are distributed from the BS to the SSs using PKM
(Privacy Key Management) protocol to ensure that only authorized SSs can receive the keys. Every WiMAX
user device is authenticated using a digital certificate or SIM
(Subscriber Identity Module). This way, WiMAX keeps user traffic from
eavesdropping and protects operator or service provider from becoming
a victim of bandwidth theft by unauthorized users.
|