Networking Guide : Network Components
Modem means modulator-demodulator. At the sending end, a modem
modulates a carrier with the
data (baseband signal) to prepare it for transmission. At the receiving end, the modulated carrier
is demodulated (i.e. converted back to the original
shape) and the
data is extracted. There are many types of
modulation techniques used in modem design, e.g. PCM, QPSK, QAM. A
modem also performs other functions, such as
digital-to-analog/analog-to-digital conversion,
compression/decompression, error correction, and
encryption/decryption.
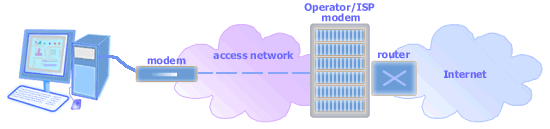
Picture: Modem in Internet access
A modem at a subscriber site communicates with the corresponding modem at her Operator or ISP.
You must connect your computer to a modem or install an internal
modem inside your computer when you want to connect to the
Internet. The type of modem that you need depends on the Internet
access method that you choose. You may need a voiceband modem, a
cable modem, an ADSL modem, or a GPRS modem. Your modem will
communicate with the corresponding modem at your ISP during an
Internet connection, transmit your computer message to the ISP
(upstream), and receive Internet content forwarded by the ISP
(downstream).
|