Networking Guide : Network Components
Hub is the central connection point in a network. Hub is used in a
network that uses star topology.
A sending computer transmits its signal to a hub, the hub then
retransmits the signal to all other computers. A passive hub
functions as a relay station that receives and retransmits signal.
An active hub functions as a repeater that regenerates signal
before retransmitting.
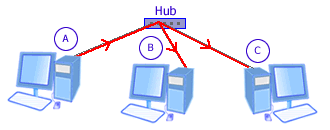
Picture: Hub
When A sends to C, the Hub receives signal from A and retransmits it to both B and C.
Only C then processes the signal.
Using a hub, the network bandwidth (capacity) is shared by all available computers,
therefore each computer only uses a portion of bandwidth. That's why hub is mostly used in small networks
where there are only a few connected devices or computers. However, hub is not required if there are
only two computers in a network. In that case, a direct connection using cable or wireless
link can be used to connect both computers.
Like hub, switch works as the central connection point in a
network. However when a switch receives a packet from a sending
computer, it examines the destination address (i.e.
MAC address of the destination
computer) from the packet header and retransmits the packet to the destination computer only.
That's possible because a switch maintains a table that maps all its ports with all connected devices' MAC addresses.
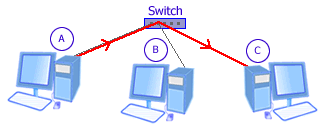
Picture: Switch
When A sends to C, the Switch receives signal from A and only retransmits it to C.
B doesn't receive the signal.
Using a switch, the whole bandwidth can be used by each connected computer.
That's why most big networks in which a large amount
of data must be transferred at any given time, use a switch instead of hub.
Switch is not always a separate device, it is very often integrated with router.
|