Networking Guide : Physical Media - Coaxial Cable
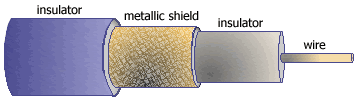
Picture: Coaxial cable (coax) structure
Coaxial cable contains a solid or stranded wire in the core
that is insulated with a dielectric layer, then protected
with a solid or braided metallic shield,
and covered with an outer insulator. Electromagnetic wave
propagation in a coaxial cable is confined within the space
between the core and the outer conductors. The structure of a
coaxial cable makes it less susceptible to interference, noise, and crosstalk
than the twisted pair cable.
Coaxial cable is often classified based on
its characteristic impedance. Most coaxial cables have
characteristic impedance of 50 or 75 Ohms. Coaxial cables in the
market are
usually named with RG prefix which may stand for Radio Grade. Each
RG type is related with certain characteristic impedance and outer
diameter. For example RG-6 which has impedance of 75 Ohms is
used for connecting cable modem or TV to a
CATV network. RG-58 (50
Ohms) is used in earlier Ethernet networks (10Base2).
Coaxial cable is terminated with RF (BNC) connectors.
|