Reference : IEEE 802 Standards
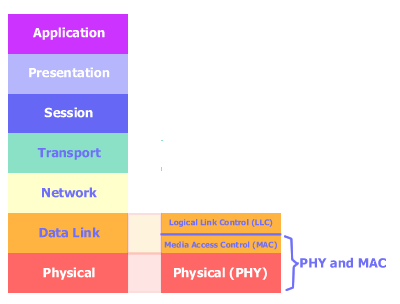
Figure: IEEE 802 scope in the OSI Model protocol
stack
The IEEE 802 standards "only" explain physical layer (PHY) and MAC sublayer in
the OSI Model.
Several IEEE 802 standards that are often mentioned in publications are
listed below:
IEEE
802.11a : Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical
Layer (PHY) Specifications � High-speed Physical Layer in the 5
GHz band. The implementation of this standard is also known as
Wireless A.
IEEE
802.11b : Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical
Layer (PHY) specifications � Higher-speed Physical Layer (PHY)
extension in the 2.4 GHz band. The implementation of this standard
is popularly known as Wi-Fi or
Wireless B.
IEEE
802.11g : Wireless LAN Medium Access
Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) specifications � Further
Higher-Speed Physical Layer Extension in the 2.4 GHz Band. The
implementation of this standard is also known as Wireless G.
IEEE
802.15.1 : Wireless Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer
(PHY) Specifications for Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs).
This standard is based on Bluetooth
specification.
IEEE
802.15.3 : Wireless Medium Access Control
(MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications for High Rate
Wireless Personal Area Networks (HR-WPANs).
IEEE
802.15.4 : Wireless Medium Access Control
(MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications for Low Rate
Wireless Personal Area Networks (LR-WPANs). This standard
refers to ZigBee specification.
IEEE 802.16 : Air Interface for Fixed Broadband Wireless Access
Systems. The implementation of
this standard is known as WiMAX.
|