Introduction to Adaptive Antenna System (AAS)
An Adaptive Antenna System (AAS) can focus its transmit energy to
the direction of a receiver. While receiving, it can focus to the direction
of the transmitting device. The technique used in AAS is known as beamforming or
beamsteering or beamshaping. It works by adjusting the width and
the angle of the antenna radiation pattern (a.k.a. the beam).
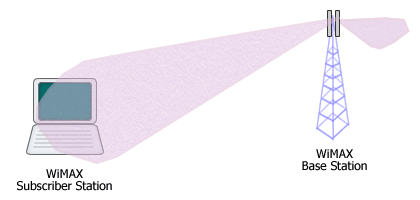
Picture. WiMAX BS with AAS beamforming capability
The main lobe is directed toward a subscriber station (SS).
Combined with multiple antennas in the Base Station (BS), AAS can be used to
serve multiple Subscriber Stations (SSs) with higher throughput.
A technique
known as SDMA (Space Division Multiple Access) is employed here
where multiple
SSs that are separated (in space) can transmit and receive at the
same time over the same sub-channel.
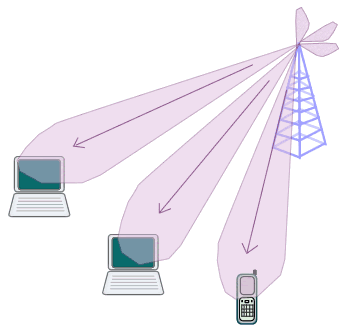
Picture. WiMAX BS with multiple antennas and AAS
AAS and multiple antennas combined in the BS can increase per user
data rate.
AAS also eliminates interference to and from other SSs and other
sources by steering the nulls to the direction of interferers.
AAS is an optional feature in WiMAX and not included in WiMAX certification. But due to its effectiveness in improving performance and
coverage especially in Mobile WiMAX case, many vendors integrate AAS capability into their products.
|