Internet Access Guide : GPRS
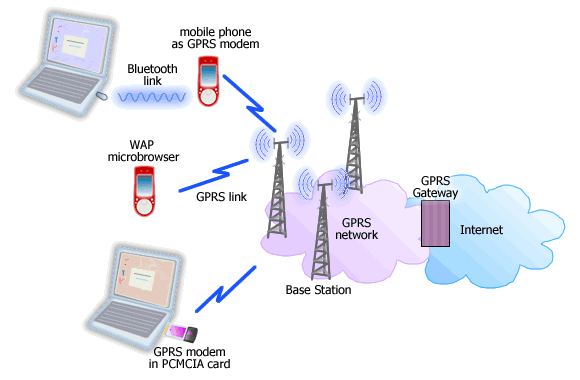
Picture: Internet access over GPRS
One may use a mobile phone, PDA, or notebook to connect to a GPRS network.
A mobile phone can be used as a GPRS modem too by linking it with computer
using Bluetooth, infrared, or serial cable.
General Packet Radio Services or GPRS is an enhancement to
GSM
or TDMA (IS-95) network. That's why GPRS
is often touted as a 2.5G technology. It uses existing cellular network
infrastructure with software upgrade at base stations and the addition of a GPRS
Gateway that connects the GPRS network to the Internet.
GPRS
as a mobile communication technology between 2G GSM and 3G WCDMA
has been serving as data bearer in mobile Internet access as well
as other applications, such as machine-to-machine communication. When the faster 3.5G HSDPA networks
and the latest 4G LTE networks are being deployed here and there,
GPRS still retains its place as a fall-back technology in areas
where the higher speed options are unavailable.
Because GPRS is a packet switched
network, a GPRS user station doesn't occupy a dedicated path during an Internet
connection. However, each end user station (e.g. mobile phone) is allocated
several time slots out of 8 GSM/TDMA available time-slots for GPRS service. Each
time slot has a maximum capacity of 14.4 kbps. Depending on how many time slots
are allocated for the downlink (from a base station to a user station) and the
uplink (from a user station to a base station), GPRS devices are divided into
multi-slot classes. A multi-slot class is often represented by the number of
downlink and uplink slots. For example, Class 10 is also known as Class 4+2.
While active slots indicate the maximum number of slots that can be allocated
for both downlink and uplink in a specific class. The following table lists
available multi-slot classes.
page 2 : GPRS device classes
page 3 : how to use GPRS
|