Internet Access Guide : Cable Modem
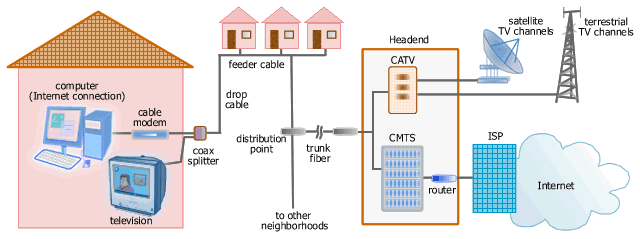
Picture: Internet access over Cable TV network
A cable modem
communicates with the corresponding modem at the cable operator site (Headend).
In Internet access using cable modem, data
(Internet) signal is delivered through HFC infrastructure which
consists of fiber optic cables from a cable TV operator site or
Head End down to a neighborhood hub and a coaxial cable from the hub to
each subscriber house. At a subscriber house, a coax splitter is used to split the drop coaxial
cable into several coaxial cables, typically one is allocated for Internet
connection and the rest for cable TV delivery. Internet signal
occupies a separate channel in the coaxial cable spectrum so it
doesn't disturb the cable TV channels.
A cable
modem at a subscriber site
communicates with the corresponding modem at the CMTS over CATV
network during an Internet connection. The communication follows DOCSIS
(Data over Cable Modem Service Interface Specification) standard. Cable Modem Termination
System (CMTS) at the Head End
contains all modems that terminate connections from all
subscribers' cable modems.
Internet access over cable TV network is delivered
through a medium (coax) which is shared by all subscribers
within the coverage of a neighborhood hub. The maximum shared data rate is
38 Mbps
downstream and 30 Mbps
upstream. Real world performance depends on how many people within a
neighborhood connect to the Internet at the same time, the
connection to backbone network, and Internet traffic load.
However most operators offer minimum downstream and upstream
rates during peak hours.
|