Internet Access Guide : Dial-Up
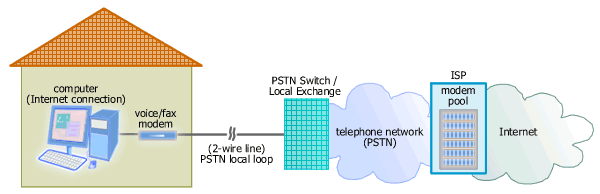
Picture: Dial-Up Internet access
A voice modem dials an ISP number that connects it to one of the
ISP's modems.
The connection goes through the telephone network.
Dial-up Internet access has been offered since the beginning of
the Internet. In dial-up access, a voiceband
modem at a subscriber site
communicates with the corresponding modem at her
ISP site over the telephone network (PSTN)
during an Internet connection. The ISP gives her a phone number
that must be dialed
to initiate communication with one of the ISP's modems. The PSTN
treats dial-up Internet signal in the same way as voice signal. Because
PSTN is a circuit switched network, a dial-up Internet subscriber
occupies a dedicated circuit during the Internet connection.
The maximum data rate that can be achieved with dial-up
Internet access depends on the type of modems employed at the
subscriber
site and at the ISP. Nowadays, most modems support either
V.90 or
V.92 modem standard. Both standards give
downstream data rate
up to
56 kbps. Upstream data rate of V.90 is 33 kbps, while V.92 can
reach 33 - 48 kbps. V.92 also supports Modem On Hold
feature, that's you can suspend your Internet session to receive a
telephone call and get back to the Internet when the call ends.
Real world performance of dial-up Internet access
depends also on the connection from the ISP to
backbone network and
Internet traffic
load.
|