Internet Access Guide : Introduction
Picture: Internet Access
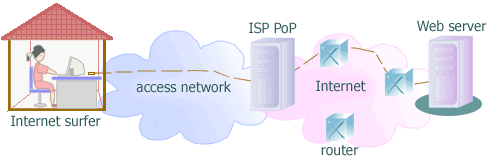
A typical Internet
user surfs the Web. Between her and the ISP PoP is the access network.
Internet access service is offered by an Internet Service Provider
(ISP). The ISP has the necessary equipment for connecting
its subscribers to the Internet such as modem pool, access server,
RADIUS server, and routers.
National ISPs usually distribute their equipment to many locations in order
to be closer to their subscribers. They have many
PoPs (Points of
Presence) that let their subscribers dial a local number
instead of a long distance number or connect over a shorter line.
An ISP's PoP is the interface between the ISP and its subscribers.
Internet access is the way a subscriber connects her modem
to her ISP's PoP. The connection may go through other operator's network,
usually telephone network (if using dial-up or
DSL modem)
or CATV network (if using cable modem).
The following are common Internet access scenarios :
- Companies pay to telecom operators for leased line (E1/T1), satellite
link, or radio link to connect their networks to their ISPs.
- Residential users mostly use dial-up modem to dial their
ISPs. Dial-up modem (i.e. V.34,
V.90, V.92) is still in widespread
use all over the world.
- Residential users who need broadband connection mostly use DSL
or cable modem.
- Public places such as university campuses, hotels, airports, and
cafs offer
Internet access through Wi-Fi hotspots.
The Wi-Fi hotspots are connected to the Internet
using leased line, DSL, or cable modem.
- Mobile workers access the Internet using their mobile phones as
modems that connect their laptops to the Internet through
GPRS
network or other types of mobile data networks such as EDGE and
EVDO. In most cases, their mobile phone operators also act as
their ISPs.
- Mobile phone users surf the Web using small screen browsers
(micro browsers) that support WAP (wireless application protocol)
over GPRS or other types of mobile data networks.
- Traveling executives connect to the Internet during
inter-continental flights through airplanes' local networks
that have broadband link to earth stations.
|